Headaches and Vision Loss – Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
A new study provides more clues about a condition that can give you headaches – and might also cause permanent vision loss. The condition? Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH).
“Idiopathic” means that the cause is unknown, although we are learning about risk factors. “Intracranial hypertension” refers to pressure in the skull.
Everyone has protective fluid around their spinal column and around the brain, called cerebrospinal fluid. But sometimes this fluid starts to build up in the skull, leading to symptoms such as headaches, vision changes (such as double vision), and a rhythmic sound in the ears (pulsatile tinnitus). It’s important to get symptoms such as these checked by your doctor as soon as possible, because they could have a number of causes, including a tumour.
In fact, intracranial hypertension itself could be a result of a brain tumour. But again, what we’re talking about today is idiopathic – we’re assuming that your doctor or specialist has already ruled out various direct causes.
Headaches from this condition are another example of why you need to get to the doctor if you have new headaches, or a significant change in your symptoms. In this case, you may start to have headaches, or the “normal” headaches you have might start to get significantly worse.
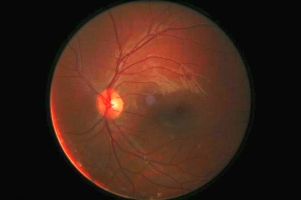
One of the possible consequences of being misdiagnosed or not getting early treatment could be a permanent loss of vision. The pressure involved actually puts pressure on your optic nerve. Vision symptoms may include partial blindness, “blind spots”, or double vision.
A recent study in the journal Neurology suggested two key risk factors. First, areas in which it was more likely for patients to be “deprived” of certain economic factors such as housing, education, and access to services, tended to have a higher risk. But even more clear was another link.
Cases of IIH have been rising – and that rise has followed the rise in obesity. This confirms an earlier study.
We also know that IIH is more common in women, ages 20-50. Both doctors and patients need to be aware of this strong link, so that they can diagnose early and get the proper treatment (which involves surgery, using a shunt to release the pressure).
Learn more:
- What is idiopathic intracranial hypertension? (National Eye Institute)
- Headache attributed to idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) (International Classification of Headache Disorders 3)
- Incidence, Prevalence, and Health Care Outcomes in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (Neurology)
- Preserving vision, easing headaches: Timely multidisciplinary care for idiopathic intracranial hypertension (Mayo Clinic)
- Brain pressure disorder that causes headache, vision problems on rise (ScienceDaily)